In this lecture, Can Aker is a guest who gave some information about construction process in Turkey.
The building is constructed by workers who are less educated people in Turkey. The most important thing while construction is work safety. The most important task of managers is to ensure work safety in construction site. Unfortunately administrations, architects, civil engineers and workers are insensitive to this issue in Turkey.
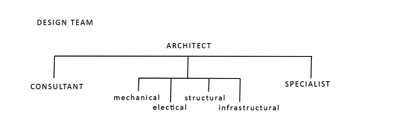
The task of the architect starts with the design process of the project. The task continues until the building is opened. The role of the architect during the construction is to coordinate mechanical, electrical, static and architectural projects. So the architect has some information about static, mechanic and electric project. It is necessary to carry out the material procurement and work schedule together. It is necessary to regard processes that affect each other. For instance there couldn’t be started to construct windows until the reinforced concrete process finished.
The expectation of the employer is that the job is finished in time and is cheap and at the same time it must be quality. It is possible if the architect has a good plan. For instance, in the middle of the construction it can be changed some material to decreasing price without changing quality (value engineering).
Project plan, work schedule plan as well as construction site should be planned. Place of containers, crane, diesel tank should be designed. Because environmental safety is important as well as work safety. There should be plans for health of workers, safety of workers as well as health of environment, night works, the sounds, the work hours etc.
There are some extra ordinary situations, which caused a pause in construction sites such as;
- Being affixed a seal by municipality
- Financial problems
- Bad planning
- Water rising
- Archeological excavation